GSM/GPRS/EDGE
Overview Mobile Network Evolution Telecommunication Technology
Lets we start with GSM (Global System for MobileCommunication)
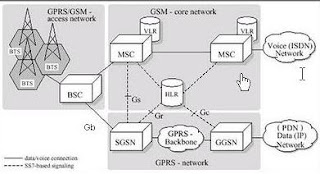
- GSM Network Architecture
We can see at picture above, this picture explain how we communicate using Mobile Station (Voice only). Just keep in your mind, the whole topology GSM. Signal from mobile station can trough BTS (Base Transciever Station) using Um interface (using air). Then BTS will sending it to BSC (Base Station Controller) using Abis interface the will be go to MSC using A interface.
Then will be check at HLR (Home Location Register) or VLR (Visitors Location Register)to check your location and the receiver. After billing and your and receiver location already knowed and valid, MSC (Mobile Switching Center) will swich and connect your mobile station to the receiver mobile station.
Gateway MSC (GMSC) :
A Gateway Mobile Switching Centre (GMSC) provides the edge function within the mobile network. It terminates the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) signalling and traffic formats and converts to protocols employed in mobile networks. For mobile terminated services, it interacts with the HLR (Home Location Register) to perform routing functions.
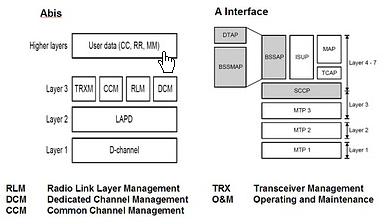
- GSM Interface and Protocols
Just read and only know
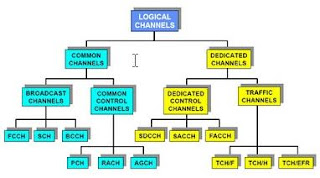
- GSM Air Interface Channel Structure
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)
- GPRS Architecture
GPRS allows mobile station to access internet. Only promises data rates from 56 up to 114 Kbps.
- These picture below are interface and protocols of GPRS network
- GPRS have 2 planes : Control and User Planes
- GPRS Core Protocol -- GTP
- GPRS User Sessions -- PDP Context
A Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context is a GPRS user session established allowing the MS and the network to exchange IP packets with QoS specifications. A PDP Context has a record of parameters, which consists of all the required information for establishing the end-to-end connection:
• PDP Type
• PDP address type
• QoS profile request (QoS parameters requested by user)
• QoS profile negotiated (QoS parameters negotiated by network)
• Authentication type (PAP or CHAP)
• DNS type (Dynamic DNS or Static DNS)
Step GSM migration to 3G, using new air-interface technology, 8 Phase Shift Keying Modulation (8-PSK) to offer 48 kbits/s per GSM timeslot. Overall offer data speed 384Kbps places EDGE, called 2.75G technology.
a. EDGE Network Architecture
MS and RAN (BTS+BSC) need to upgrade to support EDGE functionalities.
b. EDGE interface and protocols
u-ps Control Plane Protocol Stacks
Iu-ps User Plane Protocol Stacks










Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar